- Platform
- Solutions
- Modern NDR
- Resources
- Company
Platform
Modern NDR
Resources
Company
DETECTION OVERVIEW
Risk Factors
Databases are a popular target for attackers because of the valuable information that databases can contain. Before an attacker can steal this data, however, they must acquire database credentials or access the database through other means. Depending on the sensitivity of the information in the accessed database, the impact can be devastating if important, proprietary, or customer data is leaked.
The system might change the risk score for this detection.
Category
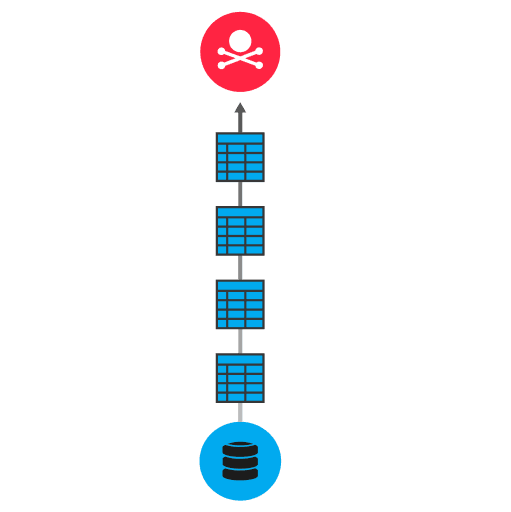
Database information can be exfiltrated by an employee with authorized access to a database or by an attacker who gains unauthorized access through malware or techniques such as SQL injection. After gaining database access, the attacker might attempt data staging. Data staging is the process of collecting and preparing data for exfiltration. Ultimately, data is transferred out of the database over protocols such as MySQL, Oracle TNS, or Microsoft TDS to unauthorized users. To hide their activity, attackers might encrypt data before they transfer it.
Implement strict rules for outbound traffic from databases that contain valuable data
Implement strict audit controls that log every database change
Review authentication methods and enforce policies for secure credentials creation and multi-factor authentication on databases
Network analysis and visibility solutions remain underrepresented in enterprises. Find out why in this preview of a new Wave report.
ExtraHop® Named a Leader in First-Ever Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Network Detection and Response
Visit this resource for more information.
This analysis exposes the critical link between an organization's lack of internal visibility and the escalating cost of compromise, demanding an urgent re-evaluation of how core business assets are protected.
Learn why you need to be wary of the claims certain network detection and response providers make about their coverage against the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
Learn how NDR from RevealX helps security teams detect and investigate more adversary TTPs in the MITRE ATT&CK framework than rule-based tools.
