- Platform
- Solutions
- Modern NDR
- Resources
- Company
Platform
Modern NDR
Resources
Company
DETECTION OVERVIEW
Risk Factors
Vulnerable devices are potentially exposed to the internet, and an unauthenticated attacker can leverage publicly-available code to exploit those devices. A successful attack enables the attacker to retrieve sensitive information, such as user credentials.
Category
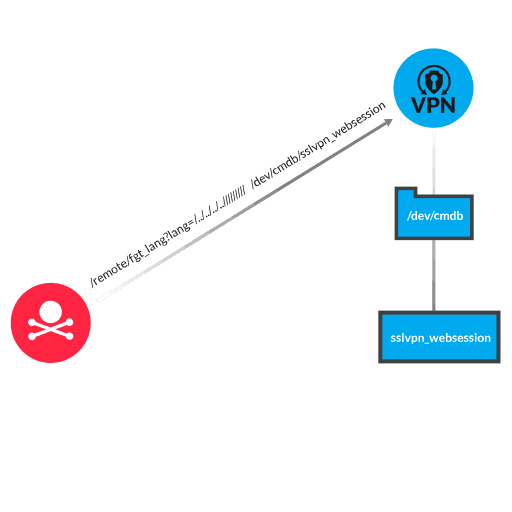
Fortinet FortiOS is a network operating system that supports security solutions offered by Fortinet. The FortiOS SSL VPN web portal (when web-mode or tunnel-mode is enabled) lacks input sanitization for URI query parameters, resulting in the exposure of information from restricted files. To exploit this vulnerability, the attacker creates a malicious HTTP request that includes a URI for an endpoint (/remote/fgt_lang), and a query parameter (lang=...). The query parameter can include a combination of traversal elements (../) and a path for reaching a restricted file. The Fortinet application processes the query parameter as trusted input, reads content from the restricted file, and returns file content to the attacker in the HTTP response. One example of a restricted file that an attacker might target is a web session file. Web session files contain information about authenticated SSL VPN users. The malicious query parameter includes traversal elements, the file path (/dev/cmdb/), and the restricted file name (sslvpn_websession). Sensitive information—such as usernames, plaintext passwords, and source IP addresses—is exposed to the attacker in the HTTP response.
Network analysis and visibility solutions remain underrepresented in enterprises. Find out why in this preview of a new Wave report.
ExtraHop® Named a Leader in First-Ever Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Network Detection and Response
Visit this resource for more information.
This analysis exposes the critical link between an organization's lack of internal visibility and the escalating cost of compromise, demanding an urgent re-evaluation of how core business assets are protected.
Learn why you need to be wary of the claims certain network detection and response providers make about their coverage against the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
Learn how NDR from RevealX helps security teams detect and investigate more adversary TTPs in the MITRE ATT&CK framework than rule-based tools.
