- Platform
- Solutions
- Modern NDR
- Resources
- Company
Platform
Modern NDR
Resources
Company
DETECTION OVERVIEW
Risk Factors
Living-off-the-land (LOL) is a method that enables attackers to evade defenses by running legitimate binary files or scripts for malicious purposes. An attacker must be familiar with LOL binaries or scripts (LOLBAS) to successfully run commands. If the attacker is able to launch a service that runs a LOLBAS on a remote device, the impact to a network depends on which command the attacker ran on the device.
Category
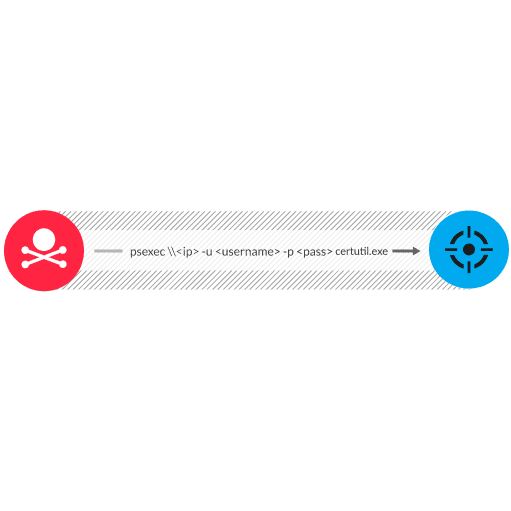
LOLBAS are tools that are signed by Microsoft and built into the Windows operating system. These tools enable helpful functionality for administrators, such as downloading, running, or compiling code. But attackers can take advantage of these tools for malicious purposes. For example, certutil.exe is a binary file that is considered to be a LOLBAS. An attacker can run certutil.exe on a remote device with tools such as PsExec. PsExec is part of the Windows Sysinternals utilities. PsExec copies the certutil.exe to a remote file share and then creates a temporary service to run both certutil.exe and commands on the victim. After successfully running the command, an attacker can make changes to the victim while evading host-based detection.
System administrators might often remotely launch services on a device. This legitimate activity can appear similar to lateral movement activity.
Disable the ability to download software utility tools such as AppLocker, unless required
Disable or remove binary files listed in the LOLBAS project unless required
Reduce the number of users that have administrator privileges
Block SMB access to restrict file sharing communications
Implement network segmentation, security zones, and firewall policies that limit how devices communicate
