- Platform
- Solutions
- Modern NDR
- Resources
- Company
Platform
Modern NDR
Resources
Company
DETECTION OVERVIEW
Risk Factors
The Apache APISIX gateway is often exposed to the internet, and this vulnerability is well known. An attacker can leverage public exploit code to gain complete control of an API gateway, launching additional attacks on the network.
Category
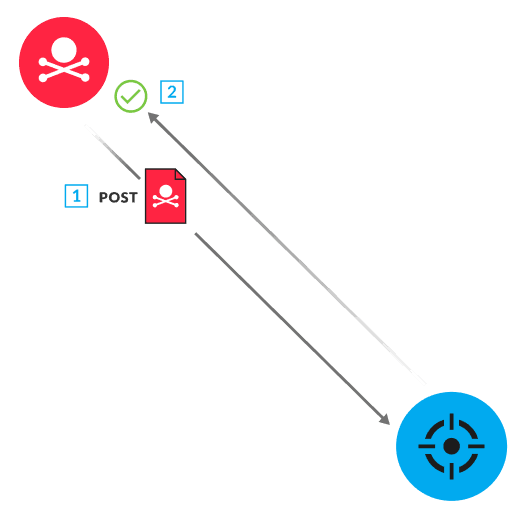
Apache APISIX is an API gateway that manages traffic for web servers. A default APISIX installation includes a batch-requests plugin, which performs actions on behalf of the user. The Admin API is restricted to local hosts. Within the default installation, the batch-requests plugin has an IP restriction bypass vulnerability that allows a remote attacker to perform administration actions on a web server, such as creating an endpoint to a malicious script. To exploit this vulnerability, an attacker sends a specially designed HTTP POST request to the plugin. This request includes the default Admin API key to perform administration actions, a payload such as a malicious script, and a forged x-real-ip value. Normally, the batch-requests plugin sets the IP address of the caller in the x-real-ip value. Instead, the plugin accepts the forged x-real-ip value, enabling the malicious POST request to be processed while bypassing the IP address restriction (1). The web server sends a response with a 200 status code and a payload that summarizes the administration actions that were completed (2).
Network analysis and visibility solutions remain underrepresented in enterprises. Find out why in this preview of a new Wave report.
ExtraHop® Named a Leader in First-Ever Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Network Detection and Response
Visit this resource for more information.
This analysis exposes the critical link between an organization's lack of internal visibility and the escalating cost of compromise, demanding an urgent re-evaluation of how core business assets are protected.
Learn why you need to be wary of the claims certain network detection and response providers make about their coverage against the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
Learn how NDR from RevealX helps security teams detect and investigate more adversary TTPs in the MITRE ATT&CK framework than rule-based tools.
