- Platform
- Solutions
- Modern NDR
- Resources
- Company
Platform
Modern NDR
Resources
Company
DETECTION OVERVIEW
Risk Factors
This vulnerability is well known, but vulnerable Windows devices might not be exposed to the internet or have IPv6 enabled. Because working exploit code is not publicly available, an attacker must write and test their own exploit code. A successful exploit can create a denial of service (DoS) on Windows 10 and Windows Server 2019.
Category
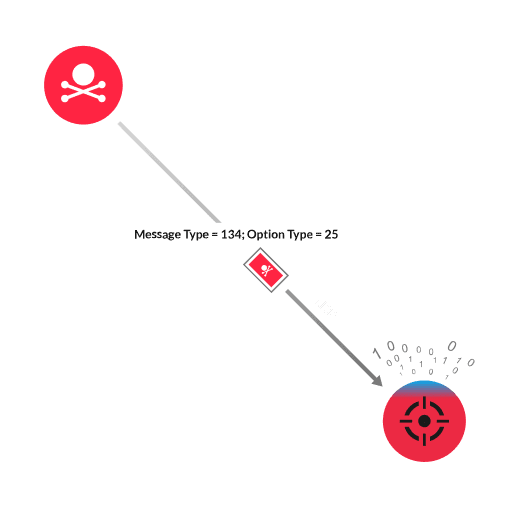
The Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) facilitates host-router discovery and DNS configuration for IPv6 addresses. NDP defines ICMPv6 message types, which helps to identify relationships between devices in an IPv6 network. One of these message types is a Router Advertisement (message type 134), which can include one or more DNS Search List (DNSSL) options (option type 31). This option provides a list of DNS name suffixes that IPv6 hosts can reference when performing DNS query searches for short, unqualified domain names. The Windows TCP/IP stack has a vulnerability in how it processes the domain names found in the DNSSL option of the ICMPv6 Router Advertisement packets. An attacker creates a malicious packet with a value larger than the specified size in the Length field of the DNSSL option. The attacker sends the malicious packet to the vulnerable Windows device. The large value causes the Windows TCP/IP stack to overrun the allocated buffer size when processing the packet data. The result is a buffer overflow that can lead to a denial of service (DoS).
Network analysis and visibility solutions remain underrepresented in enterprises. Find out why in this preview of a new Wave report.
ExtraHop® Named a Leader in First-Ever Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Network Detection and Response
Visit this resource for more information.
This analysis exposes the critical link between an organization's lack of internal visibility and the escalating cost of compromise, demanding an urgent re-evaluation of how core business assets are protected.
Learn why you need to be wary of the claims certain network detection and response providers make about their coverage against the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
Learn how NDR from RevealX helps security teams detect and investigate more adversary TTPs in the MITRE ATT&CK framework than rule-based tools.
