- Platform
- Solutions
- Modern NDR
- Resources
- Company
Platform
Modern NDR
Resources
Company
DETECTION OVERVIEW
Risk Factors
The Authentication Server Response (AS-REP) Roasting technique is publicly available and well known. Enumeration is a simple but important step taken by attackers to locate user accounts that are vulnerable to AS-REP Roasting. Attack tools make enumeration relatively easy to perform for an attacker with network access to an LDAP server. Enumeration activity typically does not negatively affect performance, but attackers can leverage this information to obtain TGT tickets and recover user account credentials.
The system might change the risk score for this detection.
Category
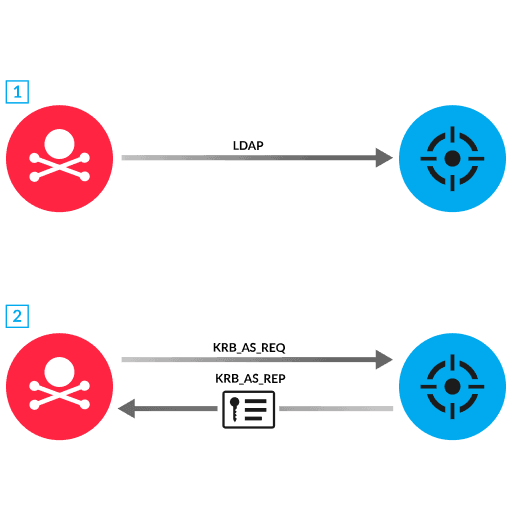
Kerberos is an authentication protocol that verifies user credentials and permissions for accessing services. When a user wants to access a service, the user account is required to pre-authenticate (by submitting credentials and an encrypted timestamp) to a Key Distribution Center (KDC) installed on a domain controller. The KDC then provides a cryptographic proof of identity known as a ticket-granting ticket (TGT), which the user can later submit to receive service tickets (TGS) for other services. However, Windows provides a way to disable the pre-authentication requirement for specific accounts. AS-REP Roasting is a technique where an attacker identifies accounts with this disabled requirement and obtains TGT tickets for these accounts for offline password cracking.
To locate accounts with disabled pre-authentication, the attacker submits an LDAP query to a domain controller to return a list of vulnerable accounts (1). To collect TGT tickets, the attacker submits an AS-REP request for the vulnerable account to the KDC, which returns a TGT to the attacker (2). If the TGT ticket is encrypted with a weak cipher algorithm, such as RC4, the TGT is more vulnerable to offline cracking, enabling the attacker to identify the user account password.
Disable weak encryption algorithms, such as the RC4 Kerberos encryption
Monitor accounts with disabled pre-authentication
Enforce a strong password policy
Network analysis and visibility solutions remain underrepresented in enterprises. Find out why in this preview of a new Wave report.
ExtraHop® Named a Leader in First-Ever Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Network Detection and Response
Visit this resource for more information.
This analysis exposes the critical link between an organization's lack of internal visibility and the escalating cost of compromise, demanding an urgent re-evaluation of how core business assets are protected.
Learn why you need to be wary of the claims certain network detection and response providers make about their coverage against the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
Learn how NDR from RevealX helps security teams detect and investigate more adversary TTPs in the MITRE ATT&CK framework than rule-based tools.
